
Every generation carries a minor change (mutation) but a variation of the original DNA template. These changes may not be visible physically but a DNA test can help you establish these highly meaningful correlations between you and your ancestors. Haplogroup R1b tells the story of West Eurasians, a.k.a. Caucasians, the segment of humanity that evolved in Western Eurasia and eventually spread out from there to conquer, dominate, and differentiate into genetically unique populations/nations all over the planet.
First, let’s find out what a haplogroup is?
A haplogroup is a group of similar haplotypes (in simple terms similar patterns) that share a common ancestor with one ore more single-nucleotide polymorphism mutation (SNP). Haplogroups are used to help trace human migration patterns and lineages throughout history. Our haplogroup gives us clues as to what our ancestors were like, where they lived, and where their descendants are today.
What is haplogroup R1b (R-M343) and what mutations in the Y-chromosome have given rise to this subclade?
The R1 Branch of the human Y chromosome tree is one of the most common haplogroups found in Europe. It has been estimated that approximately 80% of modern Europeans carry some form of this haplotype. It tells you the story of your paternal lineage since it is associated with mutations in the Y chromosome. It is also one of the oldest haplogroups. It is the evolutionary heritage of roughly 315 million people living today. The age of R1 has been estimated to be between 12,500 and 25,700 before present.
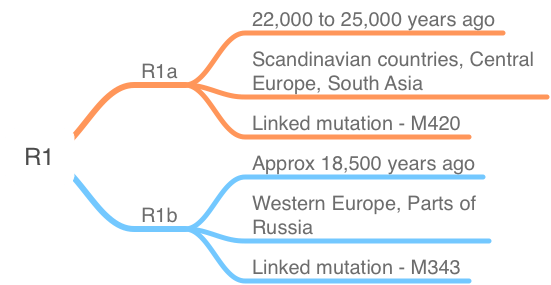
The R1 Branch of the human Y chromosome tree is one of the most common haplogroups found in Europe. It tells you the story of your paternal lineage since it is associated with mutations in the Y chromosome. It is also one of the oldest haplogroups. It is the evolutionary heritage of roughly 315 million people living today. The age of R1 has been estimated to be between 12,500 and 25,700 before present.
What is the difference between R1a and R1b haplogroups?
Haplogroup R1b was born out of haplogroup R1 in the same place as haplogroup R1a, but a few hundred years earlier. It’s now the most common Y-DNA haplogroup in Western Europe and some parts of eastern Europe as it is found in higher frequencies in the people of these regions. It is the mutations that in the Y chromosome that bring about the differences in R1a and R1b haplogroups.
Where did the Y-chromosome haplogroup (R1b) originate?
Based on recent evidence, R1b seems to have originated from Cattle herders in the region of Anatolia. R1b people are today concentrated on every continent except Antarctica. R1b (also known as Hg1 and Eu18) was first found in Northwestern Europe in high frequency in people that lived about 8,000 years ago. Thus it is thought to have spread through Central Asia, Europe, the Middle East, North Africa, and parts of Indonesia and Japan based on the distribution of shared mutations in haplogroups R1b and IJK clades.
The exact route of migration for Haplogroup R1b is still unknown but it appears to have moved from its origin in the Near East through Anatolia (modern Turkey) and then into Europe via the Balkans. From there it spread northward into Central and Northern Europe as well as eastward into Russia and Ukraine.
Is this haplogroup predominantly present in the peoples of the Caucasus?
It is certainly one of the most prevalent haplogroups among the Caucasian population. In terms of countries with more people with haplogroup R1b, Ireland has the highest frequency at over 90%, followed by Wales (84%), Scotland (82%), England (62%) and France (60%). Other countries with significant frequencies include Spain (50%), Portugal (45%), Germany (40%), Belgium (30%) and Switzerland (25%).
Does R1b have a Celtic origin?
Haplogroup R1b is associated with a wide variety of cultures, including those of Europe, the British Isles, the Arabian peninsula, and even parts of Central and South Asia. R1b has been associated with the spread of the Celtic languages from the British Isles and the Atlantic fringe.
It is now generally accepted that Celtic culture can be considered to have existed between 1000 BC and 500 AD, and it is also generally accepted that the migration period in Europe during the 5th and 6th centuries marked an end to the “Celtic” culture. However, some archaeologists consider the idea of “Celtic” culture to be older or even universal.
Even though R1b people have been instrumental in spreading the Celtic culture, it is unlikely that R1b originated from Celtic people.
Do AncestryDNA, Family tree DNA, and 23andMe compute your haplogroup?
Yes, they do and in a lot of detail. If you haven’t taken an autosomal DNA test already, it is highly recommended that you take one. It is a great investment towards uncovering more about yourself be it ancestry or for health reasons.





